Optimize Costs by Automatically Deleting Old Docker Images in Artifact Registry
Tackling Rising Storage Costs in Artifact Registry
When using a CI/CD pipeline with tools like GitHub Actions to deploy to Google Cloud Run, a new Docker image is pushed to Artifact Registry with every run. While this is a very convenient system, old images will pile up if left unchecked. Have you ever been surprised by a higher-than-expected storage bill?
This article introduces how to solve this problem using Artifact Registry's "Cleanup Policies" feature. I'll provide a step-by-step guide on how to automatically delete unnecessary old Docker images to continuously optimize your storage costs.
This guide is based on the Google Cloud Console UI as of July 2025.
1. Choosing a Strategy
First, let's consider which cleanup strategy to adopt. We compared three common approaches.
1. Delete Untagged Images Only This method deletes only untagged images, such as intermediate artifacts from the CI/CD build process. It's a safe option as all tagged versions are preserved, but the cost savings are limited.
2. Delete Images Based on Age This approach deletes images after a certain period, such as "images older than 90 days." It's simple, but with active development, you risk deleting older versions that might still be needed.
3. Keep the N Most Recent Versions and Delete the Rest This strategy retains a set number of recent versions for rollbacks while systematically deleting older ones. It offers the best balance between safety and cost savings.
For this guide, we'll adopt the third approach: "Keep the 10 most recent versions and delete all others."
2. How the Setup Works
This configuration is achieved by combining two distinct rules:
- Deletion Policy: First, we'll boldly mark all images as targets for deletion.
- Retention Policy: Next, from लड़ाईthe deletion targets, we'll create an exception to keep the 10 most recent versions.
In Artifact Registry, retention policies take precedence, so this combination allows you to safely clean up only the old images.
3. Step-by-Step Guide
Let's walk through the steps using the actual console interface.
First, log in to the Google Cloud Console and select "Artifact Registry" from the navigation menu. From the list of repositories, click on the one you want to configure.
Navigate to the repository details page, click on the CLEANUP POLICIES tab at the top, and then click the EDIT POLICIES button to open the settings screen.
This is the core of the setup. We will create two policies in order.
Policy ①: Target All Images for Deletion
Click ADD CLEANUP POLICY. For the Policy type, select Conditional deletion. For the condition, set the Tag state to Any tag state. No other changes are needed. Click DONE to save.
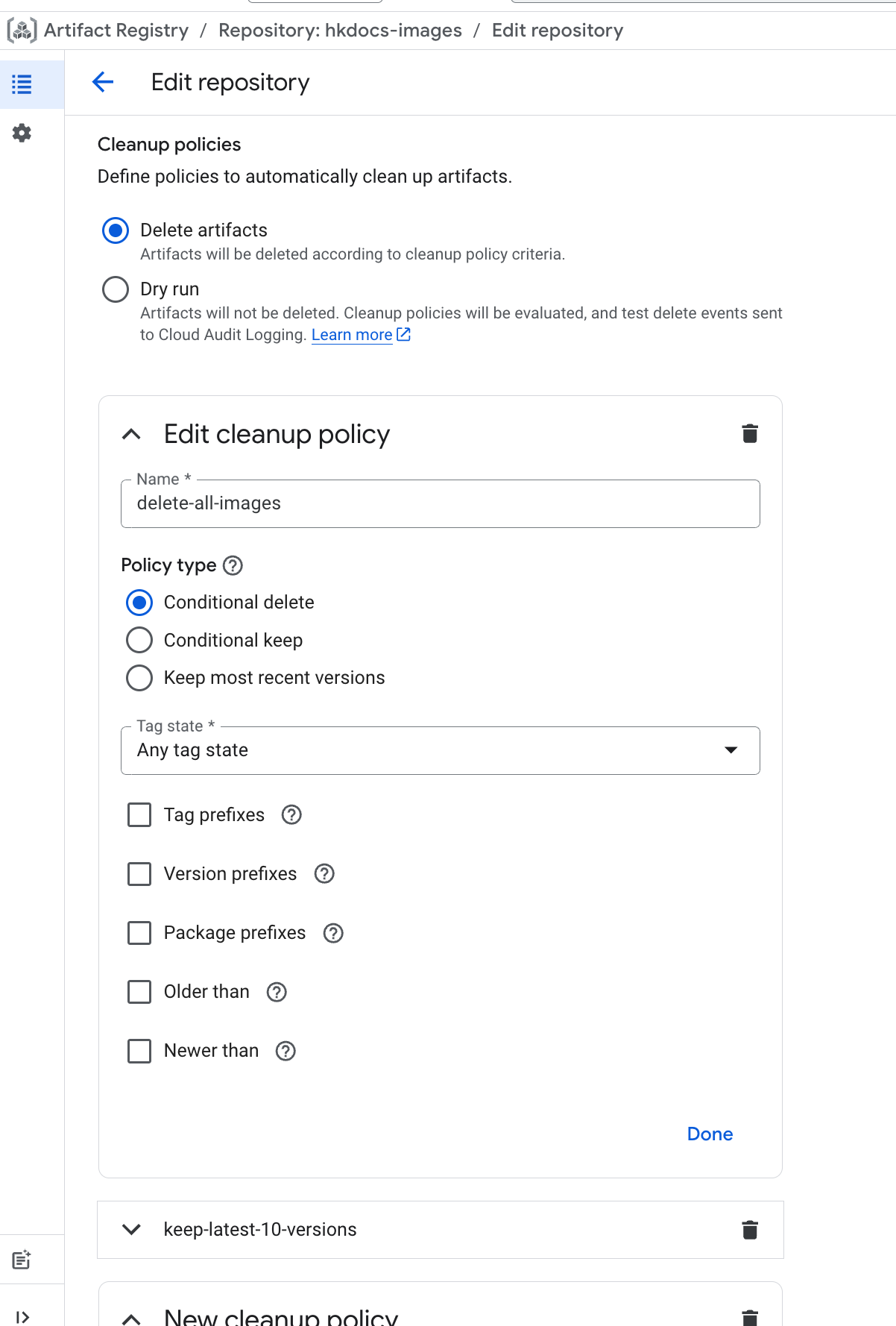
Policy ②: Protect the 10 Most Recent Versions
Next, click ADD CLEANUP POLICY again. This time, for the Policy type, select Keep most recent versions. For the Number of recent versions to keep, enter 10. Click DONE.
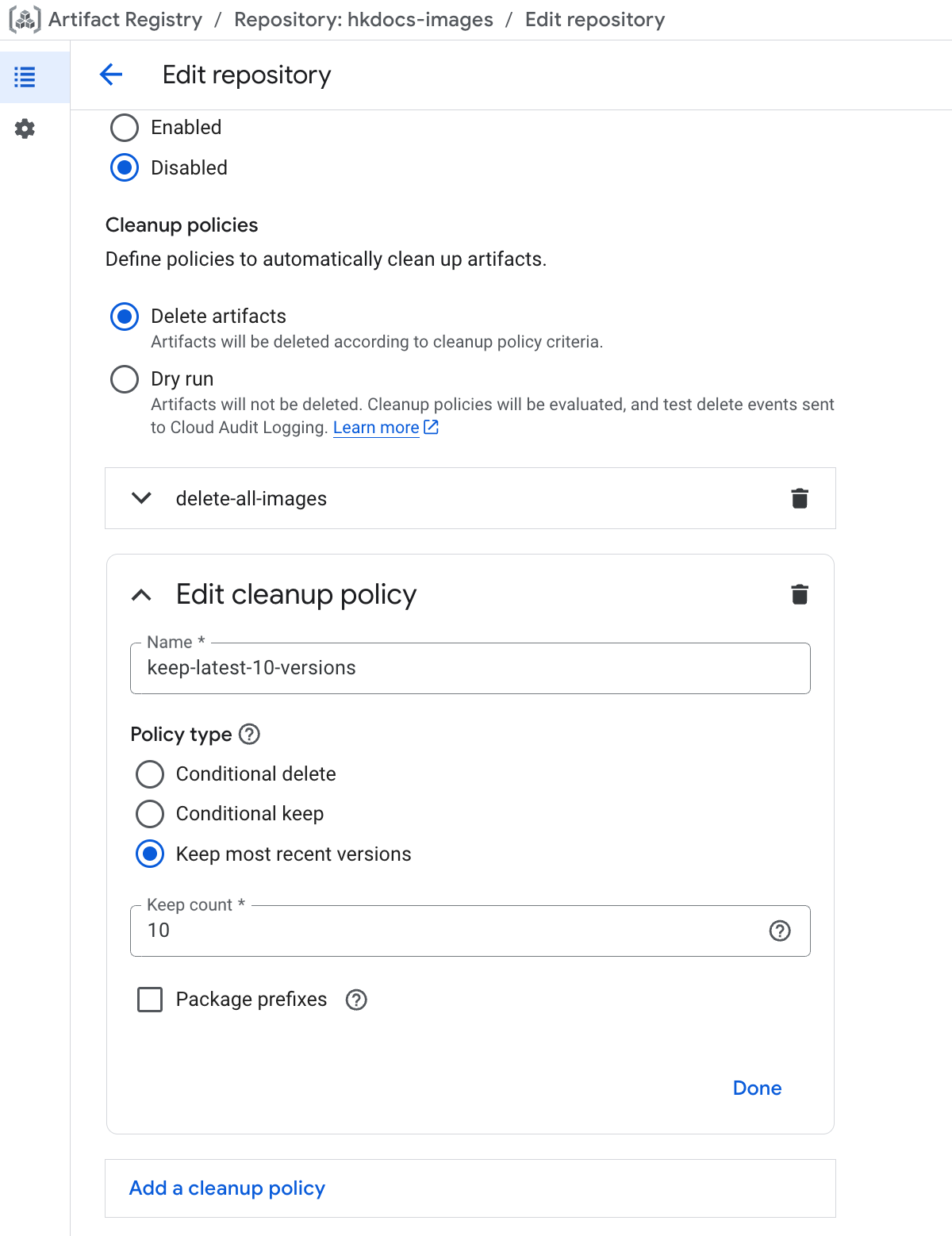
With that, the rule to "target all images but keep the 10 most recent ones" is complete.
Finally, save and enable the settings.
Instead of enabling it immediately, it's highly recommended to first select Dry run for the execution mode. In this mode, no images are actually deleted, allowing you to safely verify which images would be targeted.
After confirming that the dry run targets the correct images, return to this screen, change the execution mode to Delete artifacts, and click SAVE.
The setup is now complete. From now on, a background job will run periodically to automatically delete old images.
4. Reference: Other Configuration Patterns
Here’s a brief look at how to configure the other strategies we didn't use.
To delete untagged images only (Strategy A): This requires only one policy. Select the Policy type Conditional deletion and set the Tag state to Untagged.
To delete images older than a specific period (Strategy B):
This can also be done with a single policy. Select the Policy type Conditional deletion and set Packages uploaded before to 90 days, for example.
5. Conclusion
This article covered how to use Artifact Registry's cleanup policies to automatically delete old Docker images and save on storage costs.
Once set up, it works automatically, making it an essential task for any developer using a CI/CD pipeline. I highly recommend trying it out in your own projects.
